Table of contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Types of Fake Job Offers
- III. Identifying Red Flags
- IV. In-Depth Exploration of Red Flags
- V. Protective Measures
- A. Guarding Financial Details
- B. Refusing to Pay for Job Opportunities
- C. Reporting Suspected Frauds
- VI. Real-Life Examples
- A. Case Studies of Job Scams
- VII. The Role of Technology in Job Scams
- B. Ways to Counteract Technologically Advanced Frauds
- VIII. The Human Element in Job Scams
- A. Psychology Behind Job Scams
- IX. Government and Legal Actions
- A. Legislative Responses to Job Scams
- X. Statistics and Trends
- A. IC3 Complaint Data
- XI. Educating the Public
- A. Awareness Campaigns
- XII. Corporate Responsibility
- A. The Role of Companies in Preventing Job Scams
- XIII. International Cooperation
- A. Global Efforts to Combat Job Scams
- XIV. Future Trends in Job Scams
- A. Predictions and Projections
- XV. Conclusion
- frequently asked questions
- FAQ 1: What are the common red flags indicating a fake job offer?
- FAQ 2: How can I identify unprofessional emails from potential scammers?
- FAQ 3: Why should I be cautious about sharing financial details during a job application process?
- FAQ 4: Is it common for scammers to pose as recruiters from well-known companies?
- FAQ 5: What should I do if I suspect a job offer is fraudulent?
In an era dominated by online interactions, job seekers are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated scams. The landscape of job fraud has evolved, with scammers using various channels to present fictitious job opportunities, aiming to exploit unsuspecting individuals. This article illuminates the nuances of fake job offers and provides a comprehensive guide on how to identify and avoid falling prey to these scams.

Reverse Lookup to Search and Verify Identities — Social Catfish
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Job Frauds
Job frauds encompass deceptive practices where scammers pose as legitimate employers, offering non-existent job opportunities. These scams have become more prevalent in the digital age, exploiting the eagerness of job seekers.
B. Rising Sophistication in Job Scams
As technology advances, so do the tactics employed by scammers. The increasing sophistication of job scams requires job seekers to be vigilant and well-informed.
C. Importance of Awareness
Creating awareness about the modus operandi of job scams is crucial to empower individuals to recognize and protect themselves from potential threats.
II. Types of Fake Job Offers
A. Online Services
1. Through Bogus Websites
Scammers often create fraudulent websites that mimic legitimate job portals. Job seekers unknowingly submit their details, falling prey to identity theft.
2. Fake Job Listings on Legitimate Platforms
By infiltrating reputable job platforms, scammers post fake job listings, exploiting the credibility of these platforms to deceive job seekers.
B. Fake Emails
1. Posing as Recruiters
Fraudulent emails impersonate recruiters, enticing recipients with lucrative job offers. These emails may contain malicious links or attachments.
2. Spoofing Legitimate Companies
Scammers use advanced techniques to spoof emails, making them appear to come from well-known companies. This adds a layer of legitimacy to the fraudulent job offer.
III. Identifying Red Flags
A. Unprofessional Emails
Job scams often reveal themselves through poorly crafted emails that lack the professionalism expected from legitimate recruiters.
B. Vague Job Descriptions and Requirements
Fake job offers are characterized by ambiguous details, providing little information about the role or the qualifications required.
C. Payment Demands for Job Placement
Legitimate employers do not charge applicants for job placements. Any request for payment should raise immediate suspicion.
D. Unsolicited Job Offers
Receiving a job offer without having applied for a position is a clear indication of a potential scam.
IV. In-Depth Exploration of Red Flags
A. Analyzing Unprofessional Emails
1. Grammar and Spelling Mistakes
Scam emails often contain glaring errors in grammar and spelling, reflecting the lack of professionalism of the scammer.
2. Generic Greetings and Salutations
Personalized communication is lacking in scam emails, with generic greetings that do not address the recipient by name.
B. Deconstructing Vague Job Descriptions
1. Lack of Specifics
Scammers avoid providing detailed information about the job, making it challenging for victims to verify the legitimacy of the offer.
2. Generic Language
The use of generic language in job descriptions allows scammers to target a broader audience without tailoring their approach.
C. Unraveling Payment Demands
1. Reasons Behind Payment Requests
Scammers may concoct various reasons for demanding payment, such as processing fees or background checks, exploiting the desperation of job seekers.
2. Legitimate Hiring Practices
Understanding typical hiring processes helps individuals differentiate between legitimate requests and fraudulent demands for payment.
V. Protective Measures
A. Guarding Financial Details
Job seekers should exercise caution and avoid sharing sensitive information, such as bank account details or credentials.
B. Refusing to Pay for Job Opportunities
Under no circumstances should individuals pay money to secure a job. Legitimate employers bear the costs associated with the hiring process.
C. Reporting Suspected Frauds
1. The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3)
The IC3 serves as a crucial platform for reporting internet-related crimes, including job scams. Prompt reporting enhances collective efforts to combat fraud.
2. Law Enforcement and Emergency Contacts
In cases where immediate danger is perceived, contacting local law enforcement or emergency services is imperative for swift intervention.
VI. Real-Life Examples
A. Case Studies of Job Scams
1. Personal Experiences Shared by Victims
By delving into real-life experiences, the article aims to humanize the impact of job scams and emphasize the importance of awareness.
2. Outcomes and Consequences
Understanding the consequences of falling victim to job scams reinforces the need for preventative measures.
VII. The Role of Technology in Job Scams
A. Utilization of AI and Technology by Scammers
Scammers leverage advanced technologies, including AI, to optimize their fraudulent activities and bypass traditional security measures.
B. Ways to Counteract Technologically Advanced Frauds
1. Cybersecurity Measures for Job Seekers
Job seekers can adopt cybersecurity best practices to safeguard their personal information and mitigate the risk of falling victim to scams.
2. Industry Initiatives to Combat Scams
Collaborative efforts within industries can lead to the development of technological solutions to counteract evolving fraudulent tactics.
VIII. The Human Element in Job Scams
A. Psychology Behind Job Scams
1. Manipulative Techniques Used by Scammers
Understanding the psychological tactics employed by scammers enhances individuals’ ability to identify and resist manipulation.
2. Understanding the Emotional Toll on Victims
Job scams not only have financial repercussions but also take a toll on victims emotionally. Recognizing this aspect is crucial for providing support.
IX. Government and Legal Actions
A. Legislative Responses to Job Scams
1. Anti-Fraud Laws and Regulations
Governments play a vital role in enacting and enforcing laws aimed at preventing and punishing those engaged in fraudulent job activities.
2. Cross-Border Cooperation in Combating Scams
Given the global nature of job scams, international cooperation is essential for effective law enforcement and prosecution.
X. Statistics and Trends
A. IC3 Complaint Data
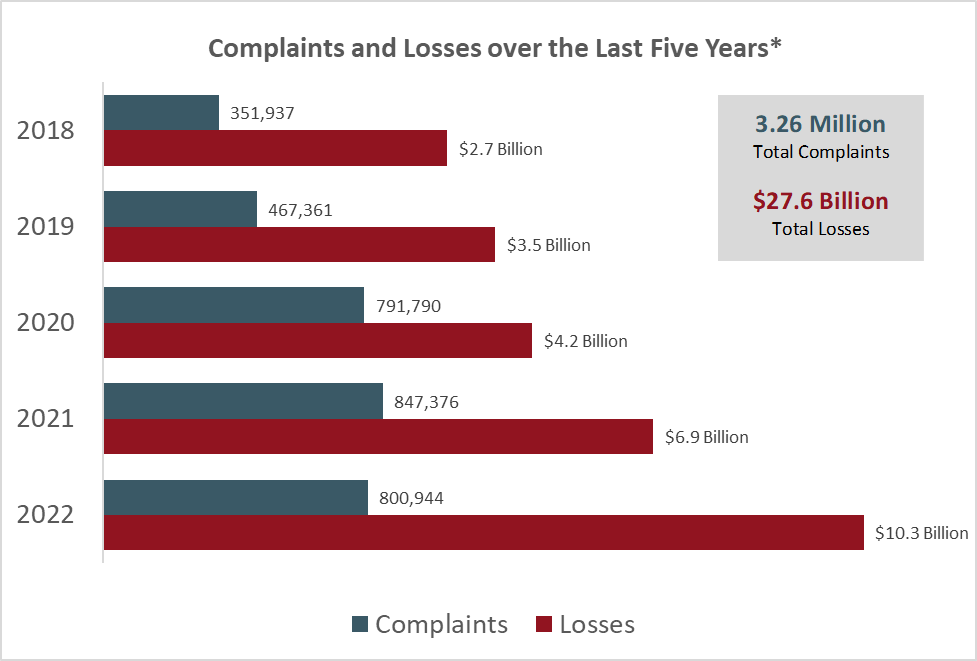
1. Yearly Complaint Trends (2018–2022)
Analyzing the yearly trends in job scams provides insights into the effectiveness of preventive measures and the adaptability of scammers.
2. Aggregate Losses Over the Years
Understanding the financial impact of job scams on victims and the economy underscores the urgency of addressing this issue.
XI. Educating the Public
A. Awareness Campaigns
1. Educational Programs for Job Seekers
Initiatives that educate job seekers about the risks and red flags associated with job scams contribute to a more informed and vigilant workforce.
2. Collaborations with Educational Institutions and Corporations
Engaging educational institutions and corporations in awareness campaigns amplifies the reach and impact of anti-fraud initiatives.
XII. Corporate Responsibility
A. The Role of Companies in Preventing Job Scams
1. Secure Job Application Processes
Companies must prioritize securing their job application processes to prevent scammers from exploiting their platforms.
2. Employee Training on Fraud Awareness
Training employees to recognize and report potential job scams adds an additional layer of defense against fraudulent activities.
XIII. International Cooperation
A. Global Efforts to Combat Job Scams
1. Interpol’s Role
Interpol’s involvement in combating cross-border job scams enhances the global community’s ability to tackle this pervasive issue.
2. Collaborative Initiatives Among Countries
International collaboration fosters a united front against job scams, pooling resources and expertise for a more effective response.
XIV. Future Trends in Job Scams
A. Predictions and Projections
1. Evolving Tactics of Scammers
Anticipating the future tactics of scammers enables individuals and organizations to stay ahead in the ongoing battle against job fraud.
2. Technological Advances in Fraudulent Activities
As technology evolves, scammers are likely to incorporate new tools and techniques into their fraudulent endeavors.
XV. Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Takeaways
Summarizing the key points reinforces the importance of vigilance in navigating the job market and avoiding potential scams.
B. The Continued Threat of Job Scams
Emphasizing that job scams are an ongoing threat encourages individuals to remain proactive in their efforts to protect themselves.
C. Empowering Individuals Through Knowledge
Knowledge is the most potent tool in the fight against job scams. Empowering individuals with information enables them to make informed decisions and safeguard their future.
frequently asked questions
FAQ 1: What are the common red flags indicating a fake job offer?
Answer: Look out for unprofessional emails, vague job descriptions, requests for payment to secure the job, and job offers appearing without an application. These are common signs that a job offer might be a scam.
FAQ 2: How can I identify unprofessional emails from potential scammers?
Answer: Unprofessional emails often contain grammar and spelling mistakes, generic greetings, and lack personalization. Legitimate recruiters maintain a professional communication standard, so any deviation should raise suspicion.
FAQ 3: Why should I be cautious about sharing financial details during a job application process?
Answer: Legitimate employers do not require sensitive financial information during the hiring process. Refrain from sharing bank account details or credentials to prevent falling victim to identity theft or financial scams.
FAQ 4: Is it common for scammers to pose as recruiters from well-known companies?
Answer: Yes, scammers frequently use advanced techniques to impersonate recruiters from reputable companies. Be cautious if you receive unsolicited job offers, especially if they seem too good to be true.
FAQ 5: What should I do if I suspect a job offer is fraudulent?
Answer: Report suspected job scams immediately to The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) at https://www.ic3.gov/ and avoid any financial transactions. In cases of immediate danger, contact local law enforcement or emergency services.
